The Future of Efficiency: How IPA and RPA are Redefining Modern Business Operations
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, digital transformation is critical for maintaining a competitive edge. Businesses are increasingly turning to automation technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) to stay ahead. RPA initially set the stage for operational efficiency by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, streamlining workflows, and reducing human error. Now, IPA is pushing the boundaries further by combining RPA with advanced artificial intelligence (AI) to manage complex, decision-driven processes. This powerful combination is transforming the way businesses operate, enabling sustained innovation and long-term growth across industries.
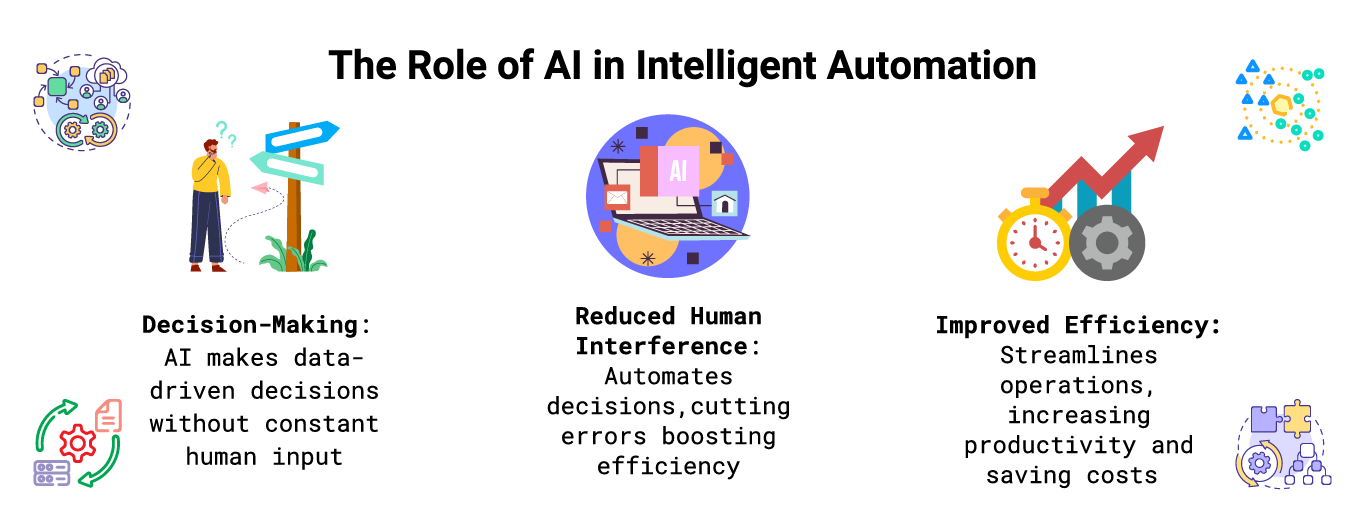
The Role of AI in Intelligent Automation
IPA leverages AI algorithms to enhance automation capabilities. Key benefits of AI integration in IPA include:
HFS Research found that organizations implementing intelligent automation have realized 28% revenue growth and 26% cost reductions.
RPA and IPA: A Powerful Combination
RPA and IPA work together to optimize business operations. RPA uses Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and User Interface (UI) interactions to automate repetitive tasks across different software systems. By mimicking human actions with scripts, RPA ensures tasks are performed consistently and accurately, leading to:
- Increased Productivity: Automates routine tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduces human error, ensuring consistent task execution.
- Scalability: Easily adapts to growing demands without significant cost increases.
IPA builds on RPA by adding AI to manage more complex tasks that need flexibility and decision-making. This combination offers:
- Data Insights: AI-driven analytics provide valuable business insights.
- Cost Reduction: Lowers operational costs by automating complex processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adapts to changes quickly, ensuring compliance and enhancing customer experiences.
Industrial Applications of IPA
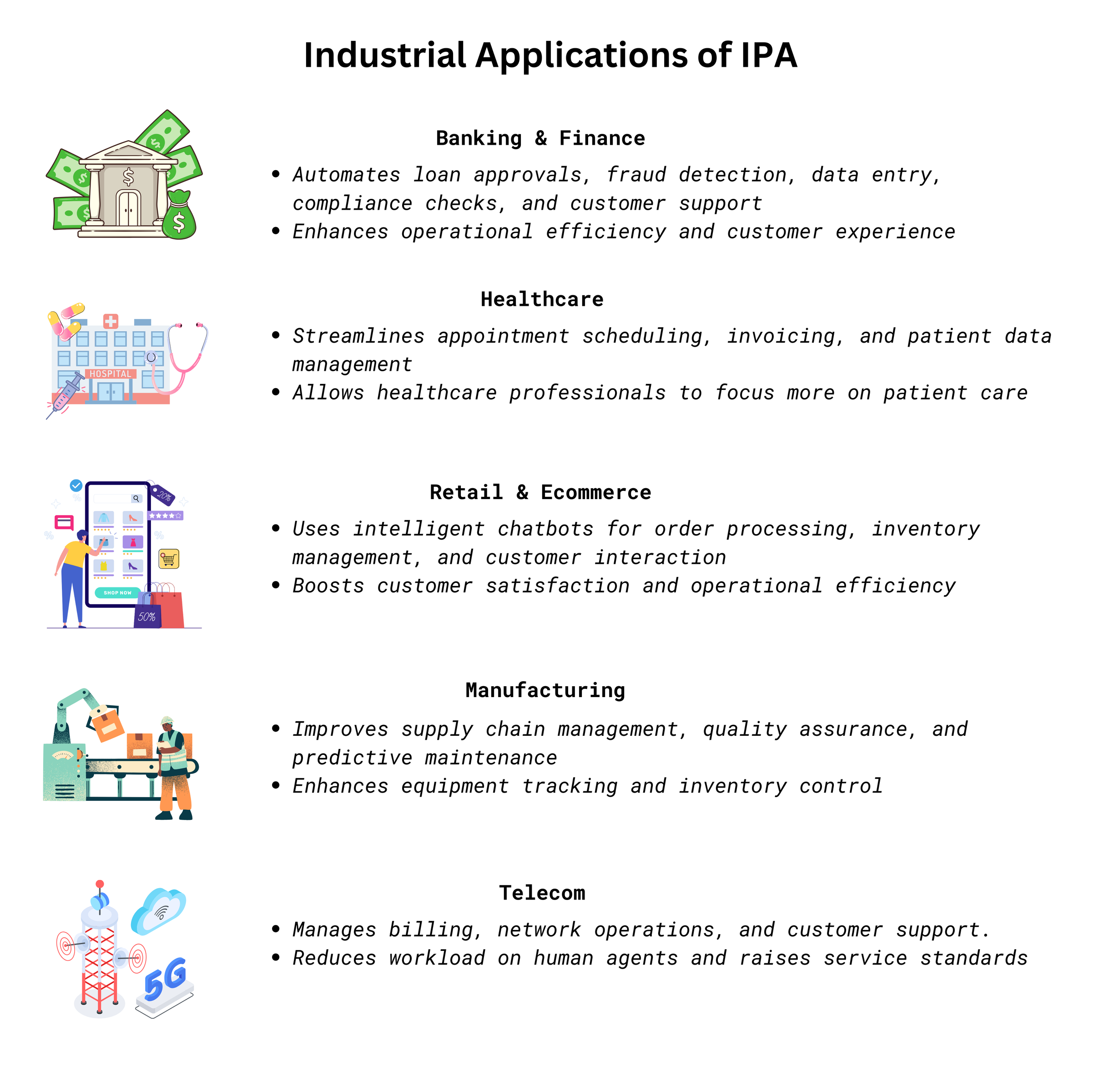
These applications demonstrate IPA's potential to revolutionize industries by combining AI and RPA. IPA’s ability to manage complex tasks and large volumes of data leads to lower costs, increased productivity, and greater employee focus on high-value work.
A 2023 McKinsey survey reinforces these benefits, with 97% of participants reporting a positive impact of automation on product quality and 95% noting significant improvements in production speed and delivery.
Key differences between RPA and IPA include:
- RPA: Ideal for structured, repetitive tasks; follows predefined rules; delivers immediate productivity boosts.
- IPA: Incorporates AI and machine learning; handles both structured and unstructured data; capable of tasks requiring judgment and continuous learning.
Core Components of IPA
IPA significantly enhances business processes by combining several critical elements. These components work together to optimize operations and enable smarter decision-making across the organization. The core components of IPA are:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automates repetitive, rule-based tasks to enhance efficiency.
- Business Process Management (BPM): Ensures that workflows are optimized, and operations run smoothly.
- Automation Tools: Provide platforms for developing, integrating, and maintaining automated workflows and bots.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Utilizes machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and cognitive computing to tackle complex challenges and adapt over time.
- Data: Involves processing structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, which AI analyzes to support decision-making and improve processes.
Exploring RPA Platforms
RPA consists of many fundamental components that work together to automate repetitive, rule-based operations, increasing efficiency and accuracy. These components differ from other platforms such as UI Path, Power Automate, and Automation Anywhere.
UiPath:
- Studio: Develops automation workflows.
- Robot: Executes tasks in attended or unattended modes.
- Orchestrator: Central platform for managing automation processes.
Power Automate:
- Triggers: Spark workflows based on specific events (e.g., email received, file created).
- Actions: Tasks executed in response to triggers (e.g., send message, update records).
- Connections: Facilitate data transfer between apps and services.
- Dynamic Content: Use variables from previous steps in actions for seamless data flow.
- Expressions: Enable data manipulation with functions and logic for better control.
- Conditional Logic: Allows workflows to adapt and branch based on specific conditions.
Automation Anywhere:
- Control Room: Central hub for bot management and performance monitoring.
- Bot Creator: Drag-and-drop workflow design interface.
- Bot Runner: Executes bots in attended or unattended modes.
- Bot Insights: Real-time bot performance analytics.
- Bot Farm: Scalable infrastructure for bot deployment.
- Bot Store: Marketplace for pre-built bots and templates.
As companies continue to adopt RPA and IPA, they are positioning themselves to lead in innovation and operational efficiency. These technologies not only streamline processes but also empower businesses to adapt quickly to new challenges and opportunities. Intelligent automation, driven by the combination of RPA and IPA, is set to be a cornerstone of future business success, delivering unparalleled growth and competitive advantage.
